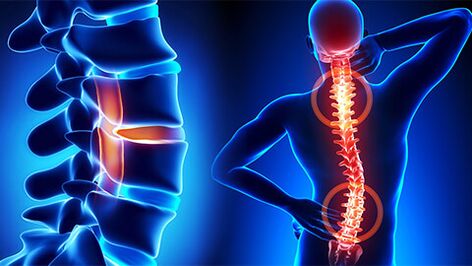
Back pain and numbness are symptoms that affect many people. The episodic appearance of these unpleasant sensations is possible for several reasons: prolonged inactivity, prolonged sitting or sleeping in the wrong position. The constant presence of such symptoms indicates the development of degenerative-dystrophic lesions of the tissues of the spine - osteochondrosis.
Osteochondrosis: what is it?
Osteochondrosis is an extremely common disease, accounting for more than half of chronic back pain cases. As a result of a combination of factors (lack of nutrients in the diet, lack of physical activity, altered metabolic processes in the body), destructive changes begin to occur in the structure of the tissues of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs, as well as thebones and ligaments associated with them. This is reflected in a change in its shape and a decrease in elasticity.
The vertebrae are compressed and the spine loses stability in the affected areas. The nerve endings of the spinal cord are pinched, as a result of which the back muscles are constantly in hypertonicity. Due to the displacement of the vertebrae, the risk of developing intervertebral bulges or hernias, as well as spondylosis (the appearance of bone processes - osteophytes) increases.
Types of osteochondrosis and stages of their development
When making a diagnosis, the place of localization of the degenerative process is taken into account. Osteochondrosis is of 4 types:
- lumbar;
- chest;
- cervical;
- generalized (when more than one department is affected).
More often than others, osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is diagnosed, since it is what explains the load on the upper half of the body.
At the initial stage, osteochondrosis is hidden under the appearance of local symptoms, so the patient does not receive timely treatment, and the disease continues to progress. The stages of sequential development of the disease are characterized by the following characteristics:
- Displacement of intervertebral discs and instability of the vertebrae.
- Reduction of the intervertebral space by destruction of the fibrous ring of the discs (compression of the vertebrae)
- Deformation of the spinal line and appearance of intervertebral bulges or hernias due to rupture of the fibrous annulus and bulging of the disc nuclei due to inadequate loading on them.
- The presence of bone growths (spondylosis), so the spine loses its flexibility. Patient movements are extremely difficult and cause severe pain and discomfort.
As in the case of any disease, the earlier osteochondrosis is diagnosed, the greater the chances of it being successfully cured. At the same time, once the patient's condition has stabilized, lifelong prevention is required to eliminate the risk of relapse - exercise and a special diet. And since most modern people are at risk for developing this condition, it's best to start a healthy morning exercise habit right now.
The reasons for the development of osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a disease that is most often diagnosed in older people due to natural causes of aging of the body and slowing down of metabolic processes. However, in the absence of physical activity and leading a predominantly "sedentary" lifestyle, this disease can develop in younger people. In this case, a weakening of the back muscles can lead to the development of a degenerative process, which disrupts the blood flow and nutrition of the tissues of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs.
Despite the prevalenceosteochondrosis, causesitsappearancenot fully understood. A combination of factors always leads to the development of an ailment, which also includes:
- malformations of the nervous and musculoskeletal systems, hereditary factors; faulty physical development;
- violation of metabolic processes in the body, improper absorption of nutrients, disruption in the work of the endocrine and digestive systems;
- vitamin and mineral deficiency in the diet, unbalanced diet, frequent dehydration;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- excess weight and increased stress on the spine, hard physical work with improper distribution of loads;
- a sedentary lifestyle, prolonged stay in uncomfortable static positions, for example, when working in an office;
- spinal injury; transferred infectious diseases, stress.
It is possible to confidently speak about the disease in the event that, due to the difficulty of access of nutrients to the tissues of the intervertebral discs and vertebrae, degenerative processes begin to develop in them. In this case, regeneration becomes completely impossible, and against the background of accompanying factors, there is a gradual destruction of the vertebrae and discs. As a result of the body's natural self-regulating processes, osteophytes can appear in the vertebrae, a kind of spines of bone tissue, which appear to cement the intervertebral space. In this case, the flexibility of the spine is lost and the movements cause pain and discomfort.
Symptoms of the disease.
If there is a general similarity, different speciesosteochondrosishave differentSymptoms and signs. . . This is due to the fact that, depending on the site of localization, as a result of pinching the vessels, painful sensations affect nearby organs and parts of the body.
For osteochondrosis of the lumbar region, pain in the lower back is characteristic with sudden movements or prolonged stay in a static position. Due to pinching of nerve endings, pain can appear in one or both legs, the nature of the pain varies from pain to pain. By assuming a comfortable position, the pain disappears.
The second most common type of osteochondrosis, cervical, is characterized by the following symptoms: the presence of a dull, crushing headache and dizziness. The unpleasant sensations intensify with the movement of the head, while the ingestion of painkillers does not relieve the pain syndrome. Pain can be given to the chest area, the sensations are similar to angina attacks, but longer. Also, there are sharp painful sensations in the hands and fingers, their numbness. Perhaps a feeling of numbness of the tongue, difficulty in the implementation of speech activity.
Thoracic osteochondrosis is relatively rare. The main reason for its development is the curvature of the spine, less often injuries. This type of disease is the most difficult to diagnose because the clinical signs are similar to those of other diseases. In addition to painful sensations in the back, which intensify with movement and flexion, with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, pain can occur in the region of the heart, liver and gastrointestinal tract. There is a feeling of numbness in the sternum muscles and the functions of the genitals are weakened.
Common osteochondrosis combines signs of various types of osteochondrosis.
How is the diagnosis made?
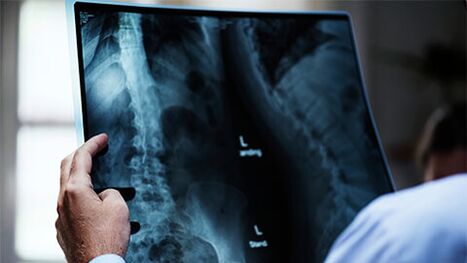
When diagnosing osteochondrosis, external examination of the patient is not enough. In addition to collecting data, a neurologist or vertebrologist prescribes the following types of examination to clarify the nature and determine the degree of damage to the spine:
- bone scan;
- Magnetic resonance;
- Computed tomography.
The final diagnosis is made based on the imaging results, after which the appropriate treatment regimen is selected.
How to treat back osteochondrosis
Since it happenedosteochondrosisa combination of several factors affectstreatmentalways includes a whole range of measurements. After the elimination of the acute condition with the help of painkillers (if there is such a need) and the appointment of a balanced diet, the following recovery methods are used:
- Exercise therapy is physical therapy, a set of exercises aimed at developing damaged areas of the spine and normalizing muscle tone. At the same time, physical activity is limited, aimed at strengthening the back muscles and restoring joint and ligament flexibility. Exercise therapy is considered the most effective method of treating osteochondrosis, but it should be done under the supervision of a specialist. There are several areas of exercise therapy, including kinesitherapy, health path, classes on special simulators. Exercise therapy has practically no limitations, since in most cases each patient is assigned an individual exercise series. You cannot participate in exercise therapy in the acute stage of the disease or with severe spinal injuries.
- Physiotherapy, which has a complex of procedures aimed at reducing pain and stimulating natural regenerative processes in the tissues of the vertebrae and discs. They use the influence of a laser, ultrasound, magnetic vibrations. As an additional method of relaxing the muscles and strengthening the body in general, as well as restoring the nervous system, a course of coniferous or pearl baths can be prescribed.
- Massage is used to relieve pain and restore blood circulation to the muscles. Massage is not prescribed in the acute stage of the disease.
- Spinal traction or traction. In this procedure, the vertebrae return to their natural position, so that the load on the spine becomes uniform.
- Reflexotherapy, when used, a specialist acts on the reflex zones and pain points, thus reducing pain. It is used in combination with massage.
- Preventive measures that give a tangible therapeutic effect include the use of special orthopedic devices - orthopedic mattresses, pillows, shoes or insoles, special corsets that hold the damaged parts of the spine in the correct position.
- Reception of chondroprotectors, which become an additional source of nutrition for damaged tissues. You should also introduce into the diet the use of gelatin-based dishes: jelly, jelly meat, aspic.
- According to the doctor's prescription, after passing the corresponding tests, foreign experts recommend taking vitamin D3, omega fatty acids and vitamin B complex.
What will happen if you don't treat osteochondrosis?
With untimely or incorrect treatment, osteochondrosis can provoke the development of the following pathologies:
- Vegetovascular dystonia.
- Lack of oxygen to the brain.
- Intervertebral hernia, which can lead to impaired motor function of the arms or legs.
Prevention methods
Prevention of osteochondrosis should be aimed at excluding factors that increase the risk of its development. This mainly applies to people who have:
- genetic predisposition to diseases of the spine;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, in which the absorption of nutrients is disturbed;
- diseases associated with metabolic disorders;
- serious infectious diseases, rickets transferred in childhood;
- spinal injury;
- overweight.
Prevention is very important for people with a sedentary lifestyle, who experience increased stress on the spine, and women who plan to have children.

The main and simplest way to prevent osteochondrosis is moderate and regular physical activity - gymnastics or swimming. It is imperative to control your posture, not to sit in unnatural positions for a long time. When doing sedentary work, it is necessary to take breaks, during which to organize physical exercises, in order to knead stiff muscles and restore blood circulation in them.
As a general rule, the usual daily movements, which are performed incorrectly, without taking into account the load they bear on the spine, become a concomitant factor in the development of osteochondrosis. For example, you should avoid lifting weights, get rid of the habit of constantly carrying a heavy bag on the same shoulder. You cannot lift heavy objects off the floor from a standing position, you must first sit down. When doing household chores (cooking, cleaning, washing, taking the correct position) stand up, do not bend over.
Another secret is to wear comfortable shoes, ideally orthopedic or with an orthopedic insole. Better to reject high heels altogether, or at least not wear them all the time.